

The new Swiss Glacier Inventory (SGI 2016) was compiled on the basis of swissTLM3D data and covers the period between 20. Another advantage is that the continuity of the data set is ensured over a long period of time, which enables the inventory to be constantly updated. Thanks to the use of swisstopo's TLM data, Switzerland's glacier inventories can be compiled much more quickly, more comprehensively and to a very high level of detail.
#Glims ice flow map update
Since 2018, GLAMOS has been using the swissTLM3D topographic landscape model to update the glacier inventory as the perimeters of the glaciers are recorded there as independent objects. Aerial photographs from swisstopo were used to create the inventories for 19. The glacier inventory of 1850 is based on a reconstruction of the glaciation expanse with moraine. Due to the great effort required in compiling them, there have only been three detailed and comparable glacier inventories for the territory of Switzerland up to now, namely for the years 1850, 19. In the case of an exceptional event, such as the breaking off of part of the Trift glacier above Saas-Grund in September 2017, swisstopo carries out extraordinary aerial surveys in consultation with the parties involved in order to document the event.Īnother important task of GLAMOS is the compilation of a glacier inventory which records the areas and contours of all Swiss glaciers.
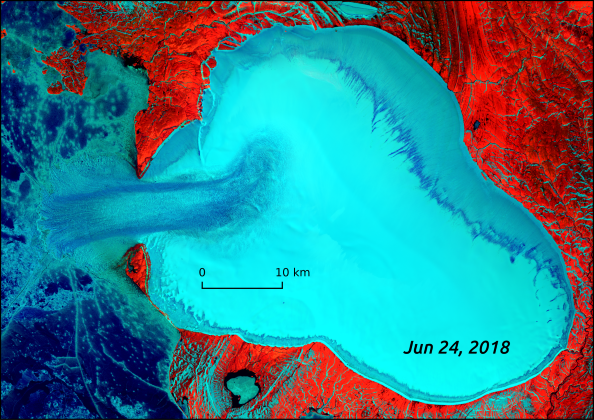
The elevation models derived from the aerial photographs make it possible to determine changes in ice volume. The resulting aerial photographs and orthophotos are used to document and visualise glacier changes and to measure glacier length and extent. TLM as a new basisĮvery year, the swisstopo flight service conducts special flights over selected glaciers, tailored to the needs of GLAMOS.
It is supported by the Federal Office for the Environment FOEN, MeteoSwiss, the Swiss Academy of Sciences SCNAT and the Federal Office of Topography swisstopo. The project is run jointly by ETH Zurich and the Universities of Fribourg and Zurich, and works closely with the Cryospheric Commission (CC). It is also used to estimate water resources, natural hazards and future sea level rises. This information is important for understanding the interaction between glaciers and the climate. Data is systematically collected on the development of area, volume, snow accumulation and ice melt, as well as glacier flow and ice temperatures. GLAMOS (Glacier Monitoring in Switzerland) observes and documents long-term glacier changes in the Swiss Alps. Glacier melt also triggers natural hazards such as floods, landslides or mudslides and causes sea levels to rise. In the longer term, however, less water is available and it is more poorly distributed, which could lead to a shortage of drinking water in the dry summer months. Initially, the melting ice provides more water for agriculture and hydroelectric power. According to measurements taken by the Glacier Monitoring network in Switzerland, two percent of Switzerland’s total ice volume disappeared again last year. Today, the melting of these glaciers is one of the most obvious consequences of climate change. FOCP: Federal Office for Civil Protectionįederal Office of Topography swisstopo Searchterm Searchterm Clear Searchtermĭuring the last Ice Age about 20,000 years ago, a large part of Switzerland was covered by glaciers.armasuisse: Federal Office for Defence Procurement.OA: Office of the Armed Forces Attorney General.swisstopo: Federal Office of Topography.Federal Department of the Environment, Transport, Energy and Communications (DETEC).Federal Department of Economic Affairs, Education and Research (EAER).Federal Department of Defence, Civil Protection and Sport (DDPS).Federal Department of Justice and Police (FDJP).Federal Department of Home Affairs (FDHA).Federal Department of Foreign Affairs (FDFA).


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
